
These are low cost and can be dipped into the liquid to allow measurement at the point of use. There are a wide variety of cups available including Ford, Zahn, Shell, and Craftsman and even different numbers based on orifice size and the range of viscosities they’re calibrated to measure. Others feature an easy conversion for the time in seconds directly into centistokes. SSU or SUS) or Saybolt Seconds Furol (abb. Examples include Saybolt Seconds Universal (abb. In some cases, the time itself is the unit of viscosity measurement. The longer the time, the higher the viscosity. The time required to completely drain the cup through the orifice is measured. Viscosity cups work on the same pour test described above but are calibrated to ensure that an accurate measurement can be taken.
At a chocolate manufacturer, they consider vegetable oil to be a thin liquid. For customers handling mostly thin liquids like water, vegetable oil would be considered a viscous liquid.
#High vs low viscosity professional
But if I were to step onto the court at a professional basketball game, you’d be more accurate to describe me as short. As an example, if you were to ask me if I’m tall, I’d say yes. The terms I used above are very subjective.
#High vs low viscosity full
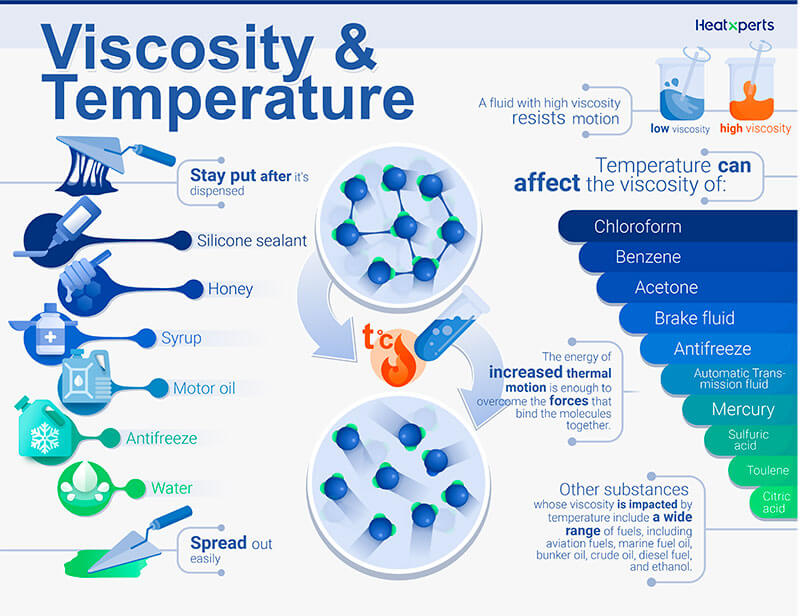
The answer is yes to the full list above, but the key is knowing, beyond a general description of “viscous”, what the liquid’s viscosity actually is. Perhaps the most important distinction between solids and liquids (at least from our pump manufacturer point of view) is “can it be moved with a pump?”. But unlike solids the viscosities of these liquids can be measured and quantified. These liquids are so thick that they begin to blur the line between liquid and solid. These are all examples of very high viscosity liquids. Peanut butter, jam, and caramel often don’t pour at all and require utensils to get them out of the container.These are all examples of high viscosity liquids. Honey, molasses, and melted chocolate are very difficult to pour and often we reach for a spoon or other utensil to speed the process.These are all examples of medium viscosity liquids. Other examples such as vegetable oil, maple syrup, and dish soap are considerably more viscous, resisting flow and pouring out more slowly.These are all examples of low viscosity or thin liquids. Water, milk, and fruit juice all flow very easily this can be observed when you pour each into a glass.Anyone who’s spent any time in the kitchen has observed a variety of liquids with a wide variety of viscosities. And you don’t need to work in a laboratory to observe this. Viscosity is a measure of a liquid’s resistance to flow.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
